如果你正在编写游戏,就得有存储和恢复游戏的功能。如果你编写的是创建图表的程序,也必须有存储/打开的功能。如果程序需要存储状态,有两种方式:
- 写入文件的序列化对象
- 写入文本文件
概述
对象有状态和行为两种属性。行为存在于类中,而状态存在于个别对象中。
如果你正在编写游戏,就得有存储和恢复游戏的功能。如果你编写的是创建图表的程序,也必须有存储/打开的功能。如果程序需要存储状态,有两种方式:
只有自己写的java程序会用到这些数据:
用序列化(serialization)。这采用了面向对象的方式来做,将被序列化的对象写到文件中,然后就可以让你的程序去文件中读取序列化的对象并把它们展开回到活生生的状态。如果数据需要被其他程序引用:
写一个纯文本文件。用其他程序可以解析的特殊字符写到文件中,例如写成用tab字符来隔的档案以便让电子表格或数据库应用程序能够应用。
序列化
序列化
下面是将对象序列化的方法步骤。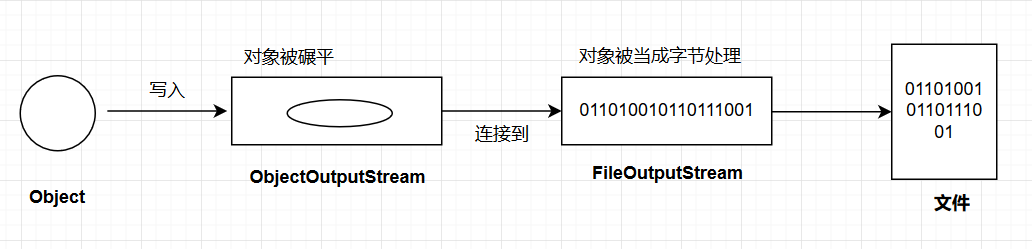
1 | //创建出FileOutputStream |
解序列化
下面是解序列化的方法步骤。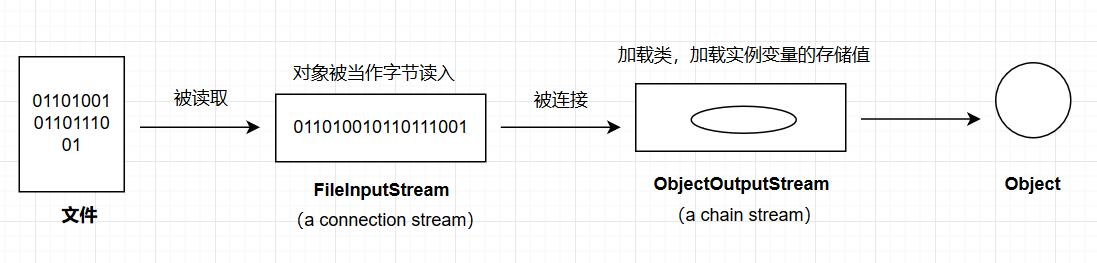
1 | //创建出FileInputStream |
接下来我们通过一个实例来进一步了解序列化的用法
代码如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
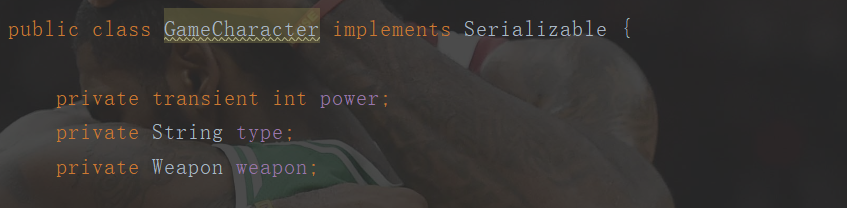
69public class GameCharacter implements Serializable {
private int power;
private String type;
private Weapon weapon;
public int getPower() {
return power;
}
public void setPower(int power) {
this.power = power;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public Weapon getWeapon() {
return weapon;
}
public void setWeapon(Weapon weapon) {
this.weapon = weapon;
}
public void useWeapon(){
System.out.println("user weapon");
}
public String toString() {
return "GameCharacter{" +
"power=" + power +
", type='" + type + '\'' +
", weapon=" + weapon +
'}';
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
GameCharacter gameCharacter = new GameCharacter(); gameCharacter.setPower(3);
gameCharacter.setType("士兵");
Weapon weapon = new Weapon(1,"长矛"); gameCharacter.setWeapon(weapon);
try {
//创建出FileOutputStream
FileOutputStream fileStream = new FileOutputStream("d://MyGame.ser");
//创建ObjectOutputStream
ObjectOutputStream os = new ObjectOutputStream(fileStream);
//写入对象
os.writeObject(gameCharacter);
//关闭ObjectOutputStream
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}}
public class Weapon implements Serializable {
int id;
String name;
public Weapon(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
}
当对象被序列化时,被该对象引用的实例 变量也会被序列化。(也就是当保存gameCharacter对象时,所有的对象都会被保存),所以如果对象被实例化时,被该对象引用的实例变量也需要实现Serializable接口。否则会抛出下面这个异常:
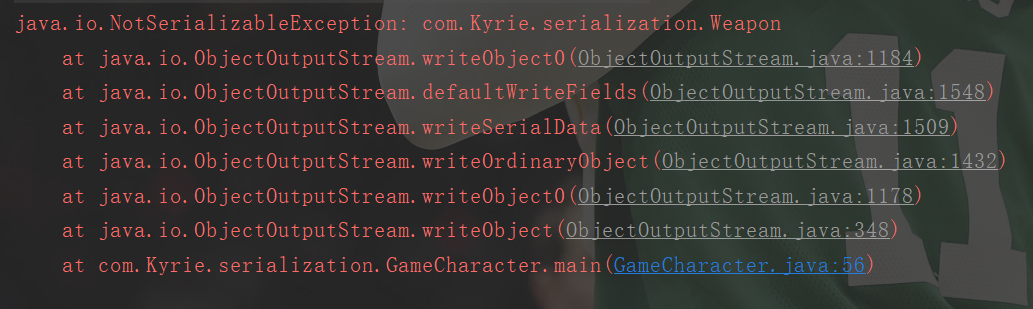 Serializable3
Serializable3如果某实例变量不能或不应该被实例化,就把它标记为transient(瞬时)的。
 Serializable4
Serializable4为什么有些变量不能被序列化?
- 可能是设计者忘记实现Serializable。
- 或者动态数据只可以在执行时求出而不能或不必储存。
- VersionID: 序列化的识别(版本控制)
如果你将对象序列化,你必须有该类才能还原和使用该对象。但若你同时修改了该类会发生什么事情?假设你尝试把GameCharacter对象带回来,而非transient的变量type已经从String被改成int。这样会严重的违反java大的类型安全性。在对象被序列化之后类有了不同的serialVersionUID,则会还原失败。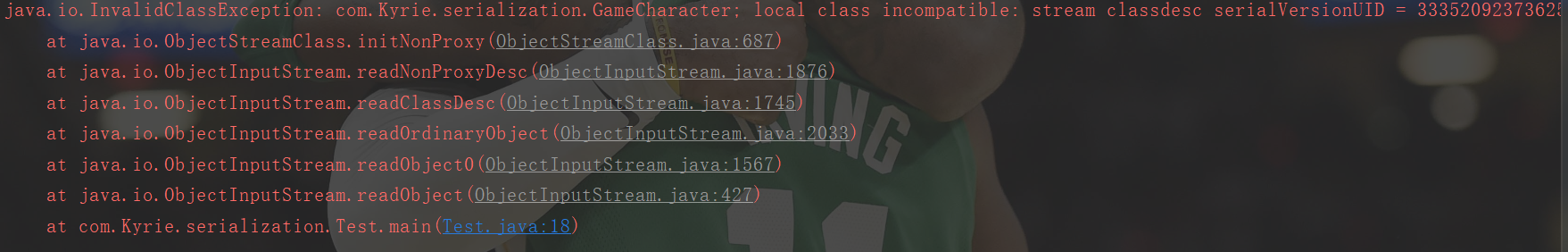 Serializable5
Serializable5
会损害序列化的修改:
- 删除实例变量
- 改变实例变量的类型
- 将非瞬时的实例变量该为瞬时的
- 改变类的继承层次
- 将类从可序列化改成不可序列化
- 将实例变量改成静态的
通常不会有事的修改:
- 加入新的实例变量(还原时会使用默认值)
- 在继承层次中加入新的类
- 从继承层次中删除类
- 改变类的继承层次
- 不会影响解序列化程序设定变量值的层次修改
- 将实例变量从瞬时改成非瞬时(会使用默认值)
如果你认为类有可能会演化,就把版本识别ID放在类中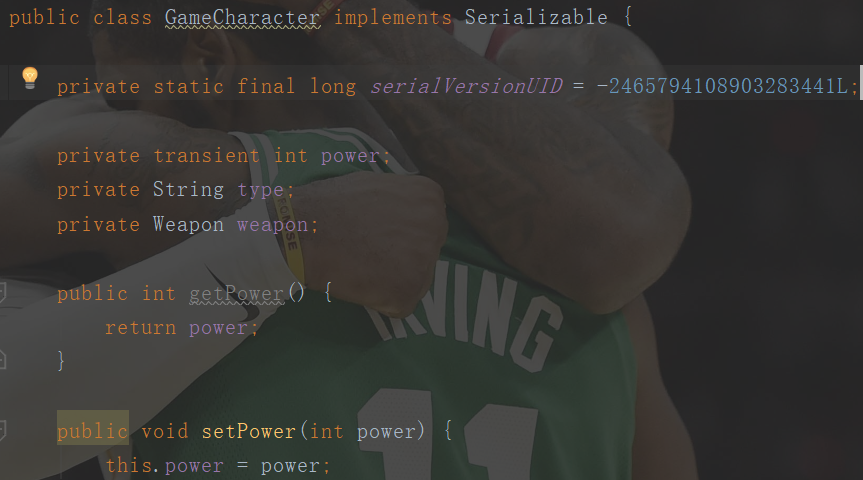
因此解决方案就是把serialVersionUID放在class中,让类在演化过程中还维持相同的ID。
但这只会在你有很小心地维护类的变动才办得到!也就是你得要对带回旧对象的任何问题负起全责。
